EIA, which stands for enzyme immune assay, and ELISA, known as enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, are both tests that are utilized by in laboratories to detect HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus). These tests are both very reliable and healthcare workers and physicians use these tests often when they are initially screening someone for HIV. If the test results of either the ELISA or the EIA are negative, additional tests are not normally required since they are so reliable. If the results happen to be positive, though, a Western blot test may be used to ensure that the result is correct and that the person in fact has HIV.
There are many similarities between the EIA and the ELISA, such as the fact they are both assay systems, but there are also some differences. For instance, the EIA is actually a group of binding assays that feature molecular recognition properties of the types of antibodies that are present. There are several types of EIA, such as a test for antigens, an immune-enzymometric assay used for antigens, a two-part sandwich EIA used to test for the antigens, and even a homogeneous EIA that tests for happens in addition to other EIA tests.
EIA tests are less expensive to administer and the equipment that is used for the tests is available at most labs. The EIA has other advantages, too, including the fact that there is no risk for biohazards, and it has the possibility to become completely automated, saving time and money. On the other hand, the ELISA is more complex as you will learn about in the next section.
What is ELISA?
First of all, the ELISA does work very similar to an EIA test since it is a test that is used in laboratories to detect if certain antibodies are present in your bloodstream. If you need to undergo this type of test, there is no special preparation that you need to do beforehand, and the health care provider will simply draw your blood from the inside of your elbow or the back of your hand to be able to test it for HIV antibodies.
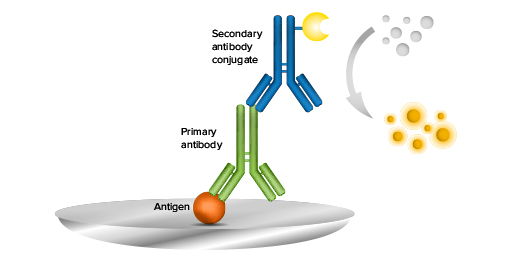
The ELISA is conducted as a plate-based assay technique that has been created to detect first certain antibodies as well as hormones, proteins, and peptides similarly to an EIA test but in an ELISA test, the antigen is isolated onto a micro-plate and then mixed with an antibody that is connected with a reporter enzyme. The activity that the reporter enzyme experiences while incubating with a certain substrate to produce a measurable product well then allow detection for the test to be completed. Basically, the most important part of an ELISA is the very specific antibody and antigen interaction with each other.
What are the Key Parts of an ELISA?
There are several key parts to an ELISA test, such as the coating solution. This is utilized to absorb the protein onto the surface of the metal plate for testing. A packing is used as a buffer with the binding sites to decrease the amount of non-specific binding occurring along with matrix interferences. Also, a detection antibody is used within the protein along with an additional substrate that is colorimetric and will catalyze the enzyme. After the testing process is completed, an ELISA reader is used to analyze all of the data from the testing process.

What is the Purpose of Enzyme Immunoassay?
During EIA testing process, enzymes are used with labeled antibodies as well as antigens to be able to detect if there are small molecules that need to be added. This type of technique utilizes the basic concept of the fact that when it comes to immunology the antigen vines with specific antibodies. Those molecules can be identified in a sample of fluid that includes hormones, proteins, or peptides. The enzymes that are normally used in this testing process are alkaline phosphates or glucose oxidase. The antigen that is in the fluid is then able to bind to a particular antibody which can then be detected by another enzyme that has coupled with an antibody. A color change will occur or if a fluorescent substance can be used that can then indicate to the laboratory technician that there is the presence of the antigen. The amount of the particular biological molecules that are being searched for can be found based on a certain color or the amount of fluorescence that can be seen at the end of the test.
When it comes to both the EIA or ELISA tests, blood is drawn from a patient by a health care provider by first using an antiseptic on the skin to kill any germs that are present before inserting a needle to draw out the blood from a vein after a band has been placed around the patient’s upper arm area. The blood will go into a syringe to be utilized for either one of these testing processes. There is only a little bit of pain from the needle being punctured into the skin but other than that, both of these testing procedures are pretty painless and will determine if there are any harmful viruses in the patient’s bloodstream.
There are a few risks that have been associated with EIA and ELISA testing procedures, such as the patient becoming light-headed from the blood being drawn from their arm or excessive bleeding occurring. Also, a hematoma can form in the area of the needle insertion, or the person can end up with an infection at the injection site.
Both the EIA and ELISA tests are imperative in testing for HIV in a patient’s bloodstream. This virus can completely destroy your immune system and is the cause of AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) which is life-threatening. There is currently no cure for this deadly disease.
It is imperative for all labs to use the best products when conducting ELISA or EIA testing procedures as well as students who are conducting experiments.